The main activities of microbiology consist in the analysis of safety and efficacy of finished products, in accordance with current legislation and through internal protocols.
For safety analyses, Challenge test, total aerobic and anaerobic counts, pathogen detection, sterility tests and Biodurden are performed. Even in the microbiological field, efficacy test that allow to support important claims such as anti-acne and anti-plaque should are performed.
Challenge test

The Challenge evaluates the microbiological stability of a product, intended as a self-preserving capacity. The method involves the contamination of the product with different species of microrganisms and the subsequent assessment of the variation of microbial load by plate counting at regular time intervals for a period of 28 days, according to ISO 11930:2012.
Market: Cosmetics, Medical devices, Raw materials.
Supported claim: Microbiological stability.
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
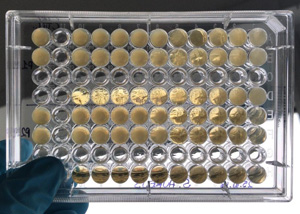
This test evaluates the minimum concentration of the tested product capable to inhibit the growth of the analysed microorganisms. The microbial strains to be used can be defined together with the customer.
Market: Cosmetics, Medical devices, Raw materials.
Supported claim: Inhibition of microbial growth.
Total aerobic and anaerobic count
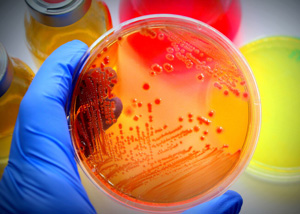 These tests allow to ensure that the manufacturing environment and the finished products do not contain harmful levels of microorganisms. Quantitative analysis of the growth of aerobic and anaerobic bacterial strains by seeding on agar according to UNI EN ISO 21149.
These tests allow to ensure that the manufacturing environment and the finished products do not contain harmful levels of microorganisms. Quantitative analysis of the growth of aerobic and anaerobic bacterial strains by seeding on agar according to UNI EN ISO 21149.
This test is mandatory for every manufactured batch of pharmaceutical, healthcare and personal care products.
Markets: Cosmetics, Medical devices, Raw materials.
Supported claim: Biosafety, Microbiological control.
Yeasts and molds total count
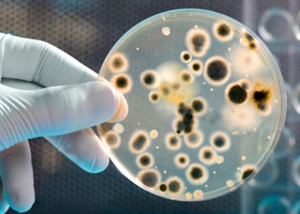
These tests allow to ensure that the manufacturing environment and the finished products do not contain harmful levels of microorganisms. Quantitative analysis of the growth of yeasts and molds by seeding on agar according to UNI EN ISO 16212.
This test is mandatory for every manufactured batch of pharmaceutical, health and personal care products.
Market: Cosmetics, Medical devices, Raw materials.
Supported claim: Biosafety, Microbiological control.
Pathogen detection

This test allows to evaluate the possible growth, in the products to be tested, of the specific strains on selective medium and positive growth controls. The target microorganisms are the following:
• Escherichia Coli (UNI EN ISO 21150);
• Candida Albicans (UNI EN ISO 18416);
• Pseudomonas aeruginosa (UNI EN ISO 22717);
• Staphylococcus aureus (UNI EN ISO 22718).
Markets: Cosmetics, Medical devices, Raw materials.
Supported claim: Microbiological biosafety.
Bioburden
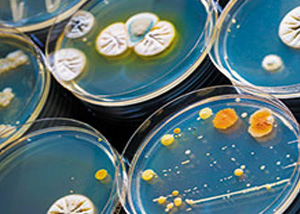 This test analyses the presence of aerobic microorganisms on non-sterile products, according to the European Pharmacopoeia 2.6.12. guideline.A defined amount of the substance to be tested is properly diluted and suspended in suitable microbiological mediums, to assess any possible growth of selected microorganisms. In particular, the following specific strains are examined:
This test analyses the presence of aerobic microorganisms on non-sterile products, according to the European Pharmacopoeia 2.6.12. guideline.A defined amount of the substance to be tested is properly diluted and suspended in suitable microbiological mediums, to assess any possible growth of selected microorganisms. In particular, the following specific strains are examined:
• Staphylococcus aureus;
• Escherichia coli;
• Bacillus subtilis;
• Candida albicans;
• Aspergillus niger;
The aim of bioburden testing is to measure the total number of viable microorganisms (total microbial count) on a raw material or finished product prior to its sterilization before use.
Markets: Cosmetics, Medical devices, Raw materials.
Supported claim: Microbiological biosafety.
Anti-plaque and anti-halitose efficacy

These tests involve the contact of the product to be tested with suspensions of some of the main bacteria responsible for dental plaque and halitose. At the end of the incubation, according to the use of the product, the efficacy of the product itself is tested by analysing the growth inhibition of specific microbial strains.
Market: Cosmetics, Medical devices, Raw materials.
Supported claim: Anti- plaque efficacy, anti-halitose efficacy.
Anti- acnes efficacy
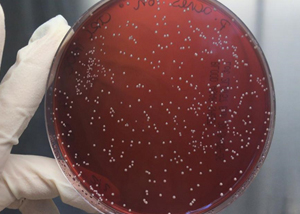
The evaluation of the anti-acnes activity of a product is based on two different assays. The first test, strictly microbiological, assesses the ability of the product to inhibit the anaerobic growth of the main bacterium responsible for the inflammatory process related to the acnes (Propionibacterium acnes).
With the second test, the levels of an inflammatory marker induced by the Propionibacterium acnes strain on cell cultures are evaluated.
Markets: Cosmetics, Medical devices, Raw materials.
Supported claim: Anti-acnes.
Sterility test
 This test assesses the sterility of sterile products in terms of presence of specific microorganisms, according to the European Pharmacopoeia 2.6.1. guideline.
This test assesses the sterility of sterile products in terms of presence of specific microorganisms, according to the European Pharmacopoeia 2.6.1. guideline.
A defined amount of the substance to be tested is properly diluted and suspended in suitable microbiological media, to assess any possible growth of selected microorganisms. In particular, the following specific strains are examined:
• Staphylococcus aureus;
• Escherichia coli;
• Bacillus subtilis;
• Candida albicans;
• Aspergillus niger.
This test is applied to substances, preparations or articles which are required to be sterile.
Market: Cosmetics, Medical devices, Raw materials.
Supported claim: Microbiological biosafety.
Bacterial adhesion
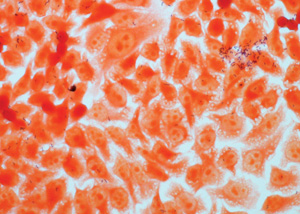
The assay evaluates the ability of a product to reduce the adhesion of specific bacterial strains into a cell monolayer using molecular biology techniques.
The effectiveness of the product is defined by the treatment of a co-culture of human cells and bacteria, the count of living microorganisms on selective plates and the identification of the adherent bacteria in the cell culture.
Markets: Cosmetics, Medical devices, Raw materials.
Supported claim: Counteracts the bacterial adhesion, Protection of skin/mucosae.
Bacterial endotoxins detection test (LAL test)

Bacterial endotoxin testing is used to identify and quantify endotoxins originating from gram-negative bacteria using the amebocyte lysate from the Limulus Polyphemus. The identification of endotoxins levels is fundamental for the biosafety of the product and for its marketing. The “Chromogenic Kinetic” method is performed according to the guidelines of the “European Pharmacopoeia 8th ed. 2014:2.6.14. Bacterial Endotoxins” and the “USP 38th ed. 2014: <85> Bacterial Endotoxins Test; <161> Transfusion and infusion assembles and similar medical devices”.
Market: Medical devices, Raw materials.
Supported claim: Biosafety.
